Elasticity of Demand: A measure of how consumers react to a change in price
Elastic demand
1.demand that is very sensitive to a change in price
2.product is not a necessity
3.there are available substitutes
4.always greater than 1
ex. soda/steak/fur coat
Inelastic demand
1.demand that is not very sensitive to a change in price
2.product is a necessity
3.little to no substitutes
4.always less than 1
ex. gas, insulin
Unitary elastic
Perfect society/always equal to 1
Total revenue: total amount of money a company receives from selling goods and services
Price x Quantity = Total revenue
Marginal revenue: additional income from selling one or more unit of a good
Fixed cost: it is a cost that does not change no matter how much of a good is produced
Variable cost: it is a cost that rises or falls depending upon how much is produced
TFC + TVC = TC
AFC + AVC = ATC
TFC/Q = AFC
TVC/Q = AVC
TC/Q = ATC
AFC x Q = TFC
AVC x Q = TVC
Marginal cost = new TC - old TC
output = quantity
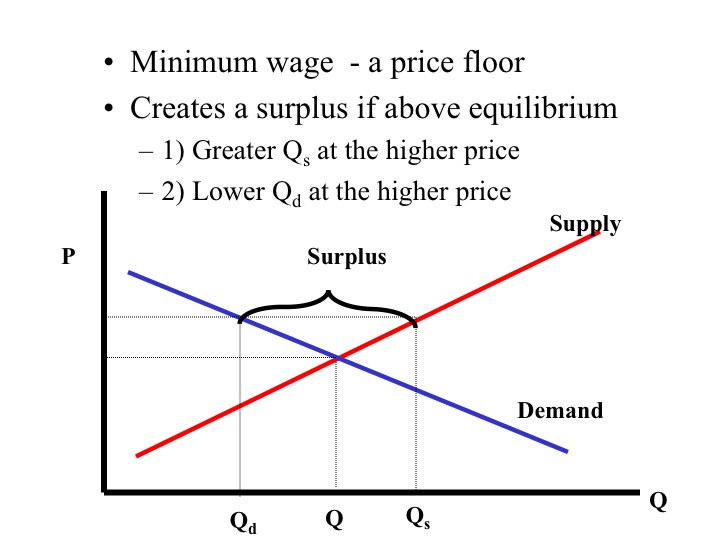
Equilibrium: point at which the supply curve and demand curve intersect
Excess Demand: where quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied (shortage); consumers can not get the quantity of item they desire
Price ceiling: found below equilibrium; occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be (ex. rent control)
Price floor- lowest legal price of a commodity can be sold at used by the government to prevent prices from becoming too low.
QD>QS excess demands (ex.rent) shortage
QS>QD excess supply/ creates a surplus